Page History
...
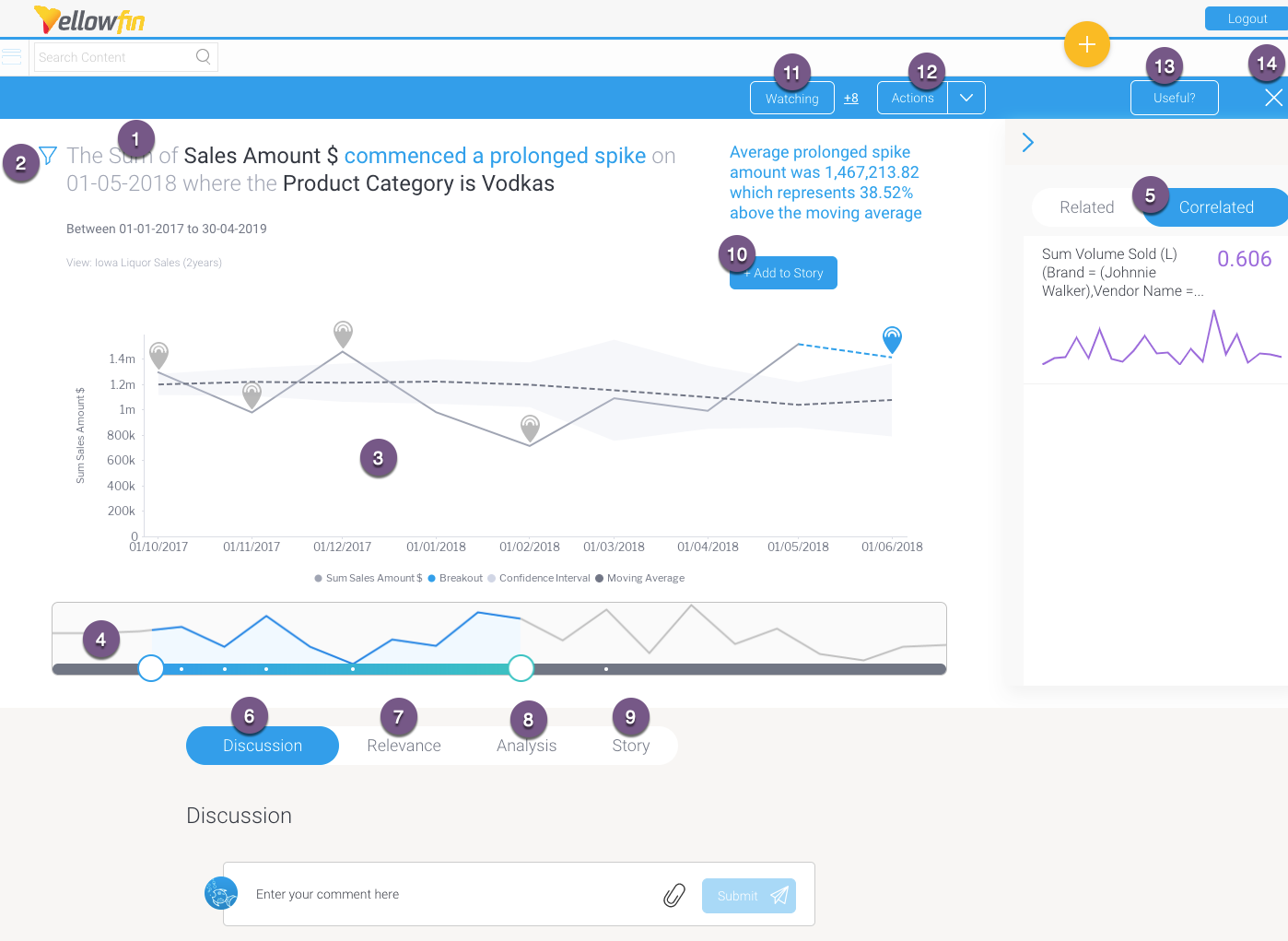
Below is an example of an outlier detection signal. Note that the main Signal chart and some other details will differ according to the different types of Signals.
Number | Signals function |
|---|---|
1 | The auto generated narrative describes the nature of the Signal, along with the time window in which it occurred. Tip: Color foreshadowing is applied to highlight good (as blue) or bad (orange) results. |
| 2 | This filter icon shows that this Signal is filtered, meaning it’s a result of a subset of the filtered data. Click on it to view the filter values. |
3 | This is the Signal time-series chart that shows the history of the specific metric - dimension combination. It displays the main Signal annotation, along with other related Signals that have occurred during that time line. You can use the annotations to learn about each of these Signals, and even explore the previous ones. (These time series charts will differ depending on the type of analysis.) Click here for more information. |
4 | The time slider that lets you expand or reduce the time window of the time-series chart. Signal annotations appearing in the time series chart are also visible in the time slider (presented as white dots). |
5 | This right side panel offers options to compare the main time-series chart with other related or correlated data charts. Click here to learn more. |
6 | The Discussion tab lets you leave comments and collaborate with other users on this Signal. |
7 | The Relevance chart depicts the importance of the Signals data in relation to all other data that the user has access to. |
8 | The Analysis tab provides automatically-generated visualizations and narratives about possible underlying causes. Yellowfin Assisted Insights functionality is utilized here to perform additional analysis on the Signal to explain why a signal has occurred. |
9 | The Story tab displays all the stories that the current Signal’s main time series chart is added to; there could be any number of linked stories. Readers can read published stories, or if in draft mode, users with collaboration access can view or edit these stories. Note: Must have Yellowfin Stories to see this feature. Click here to learn more about it. |
10 | The +Add to Story button takes a screenshot of the time series chart (in its current state) and adds it to a specified story. Learn more about this process below. Note: Must have Yellowfin Stories to see this feature. |
11 | This Watch button lets you watch/unwatch the Signal. This adds the Signal to your watch list, and sends alerts when other users interact with this Signal. |
| 12 | This Actions buttons lets you perform a number of actions on this Signal, such as owning or assigning it, sharing it, dismissing or closing the Signal. These interactions are covered here in detail. |
13 | Rate the usefulness of the Signal. Click here to learn more. |
14 | Exit the Signals detail page. |
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
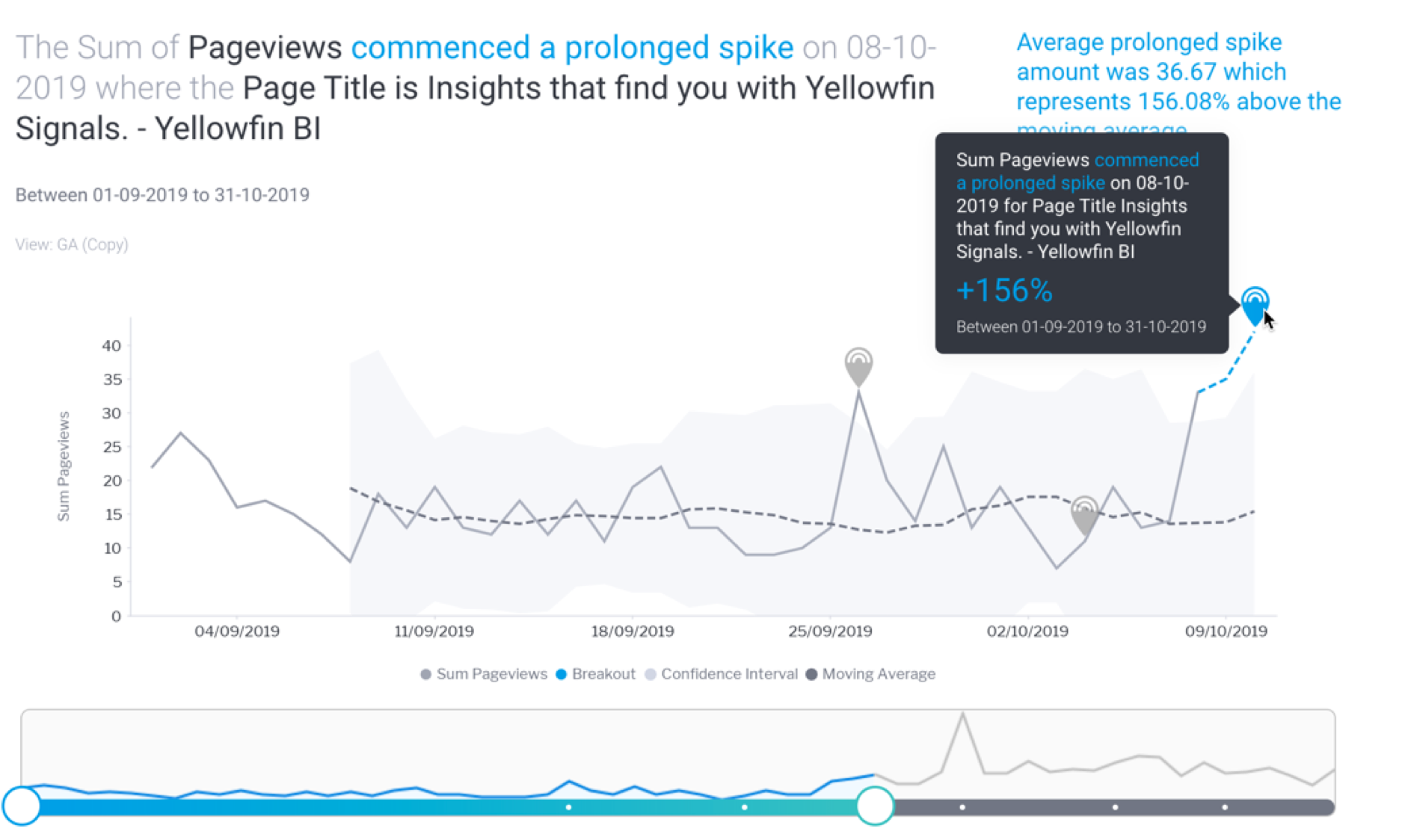
Signals time series chart
...
The Signal time-series chart shows the history of the specific metric - dimension combination. These time series charts will differ depending on the type of analysis.
Signal annotations
Main annotations
Hover over the main Signal annotation; this will bring up a tooltip that displays information on the Signal.
Other Signals annotation
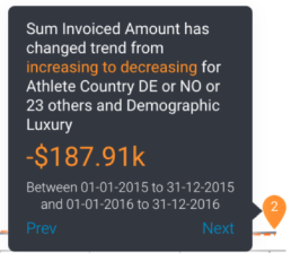
Other previously generated Signals are also visible as annotations on the time series chart. These are Signals that occur in the same time window, for the same dimension granularity. You can view the detail of that signal by hovering over the signal annotation. You can click on the Explore button to open the Signal page for that Signal.
Chart analysis
The time series chart displays different types of analysis based on the nature of the Signal.
Moving Average
The moving average calculated for Signals follows a particular calculation, and therefore will be different from the moving average calculated on a report. This is because the Signal algorithms incorporate a smoothing mechanism to limit the impact of outlier values (such as Spike, Drops) on the shape of the moving average curve. So the curves are unlikely to ever look the same, especially in the presence of one or more outliers.
Note that the Signal moving average and report moving average will be the same the first time the Signal is recorded in the analyzed time period.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...