Along with various other data source connections, Yellowfin also provides you with the option to create a JNDI (Java Naming & Directory Interface) data source. This type of connection can be used for a number of reasons, including migrating your application between different environments, such as development, integration, test or production, or connecting to an external directory service.
A JNDI data source connection is set up outside of Yellowfin. You will need to reference a connection to a database in an external configuration file in Tomcat, where all the database settings are set up.
In our example, we will use a MySQL database, named "classicmodels", to establish a JNDI connection with.

To declare a JNDI Data Source for the MySQL database above, create a Resource XML element with the following content:
<Resource name="jdbc/classicmodels" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" maxActive="100" maxIdle="30" maxWait="10000" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/classicmodels" username="root" password="root" /> |
Add this element inside the root element <Context> in a context.xml file. There two locations where the context.xml file can reside (create one if it doesn't exist):
Add the following declaration into the web.xml file (appserver\webapps\ROOT\WEB-INF\web.xml):
<resource-ref> <description>DB Connection</description> <res-ref-name>jdbc/classicmodels</res-ref-name> <res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type> <res-auth>Container</res-auth> </resource-ref> |
This is necessary in order to make the JNDI data source available to the application under the specified namespace jdbc/classicmodels.
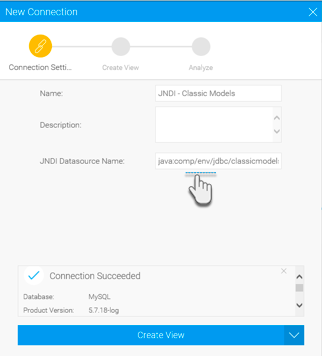
We can look up the configured JNDI data source using our example of jdbc/classicmodels and referring context via java:comp/env, for example:
java:comp/env/jdbc/classicmodels