Page History
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
Here's a step-by-step tutorial to help you set up your development environment.
- Get Download and set up Eclipse for EE developers. Note: This is Yellowfin's recommendation, however these steps can be applied in case of other IDEs as wellbut you can use your preferred IDE.
- Install the Tomcat plugin if plugin, if it isn't already bundled with the installation.
- Install the version of Yellowfin to be be used for development. It's ideal to get the latest version, so that more functionality is supported, allowing you to create advanced plugins Note: We suggest getting the latest version for increased productivity.
- Start up Yellowfin to extract the WAR file.
Create a Plugin Project
Here's what to do when you want These steps will help you to create a new project for your Java plugin.
- Once On starting Eclipse is started, create a new Java project.
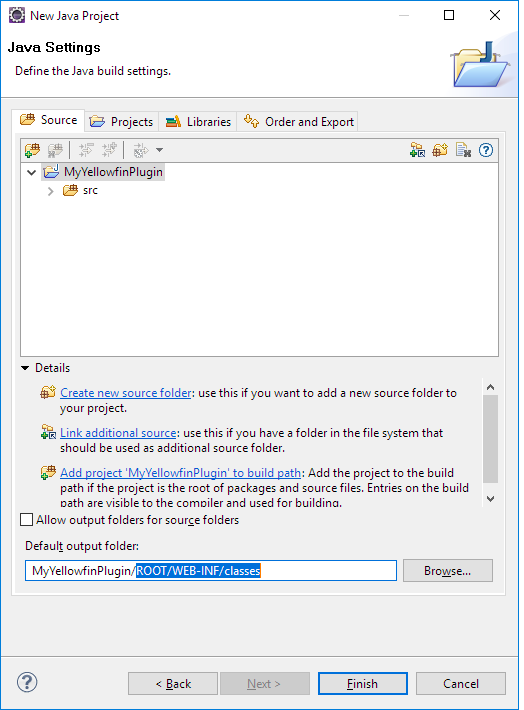
- Enter the project name and ensure you select a JRE compatible with the your version of Yellowfin.
- Click Next and change the default output folder to <project-name>/ROOT/WEB-INF/classes.
- Click Finish.
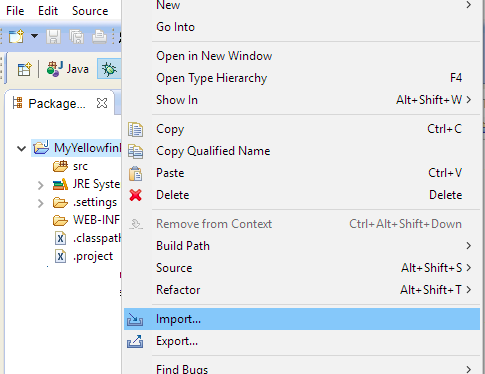
- Import files from the installed Yellowfin .instance:
- Right-click on the project project and select Import.
- Select File System and click Next.
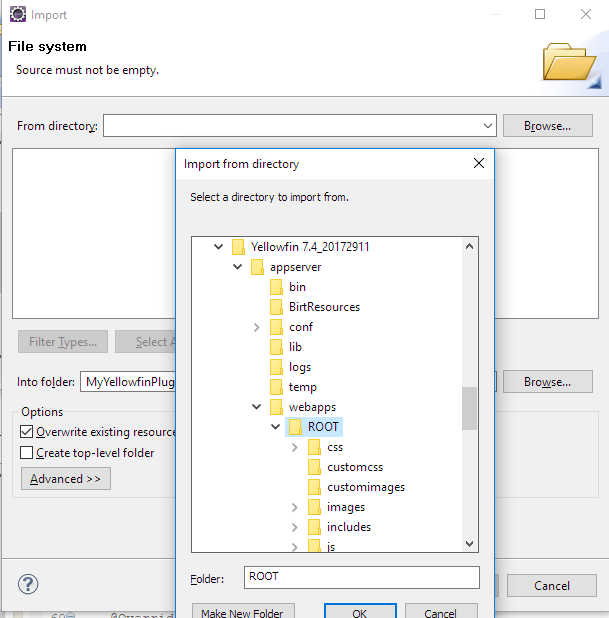
- Navigate to appserver/webapps/ROOT in the Yellowfin install directory. Select ROOT and click OK.
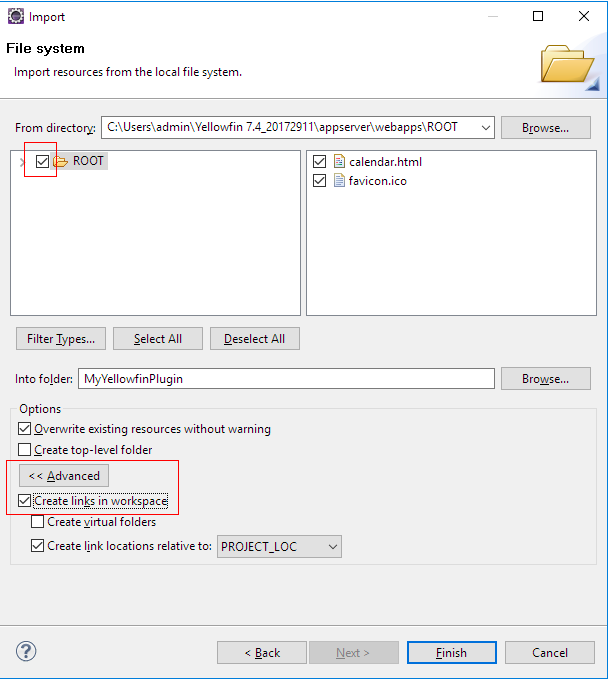
- Select everything under ROOT and in the Advanced section, select the Create Create links in workspace checkbox.
- Click Finish. Files from the installed Yellowfin get will be linked to the plugin this project.
- Right-click on the project project and select Import.
...
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Configure the Project
Follow these steps to configure your project.
- Right-click on the project and select Build Path > Configure Build Path and from the menu. Then select the Libraries tab.
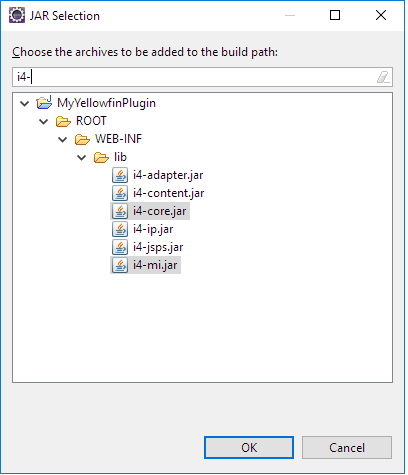
- Click Click the Add JARs and button and type "i4" into the search bar. From the results, select i4 i4-core.jar and i4-mi.jar from your plugin project.
- Click OK to save this and OK again in the build path config window.
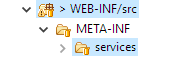
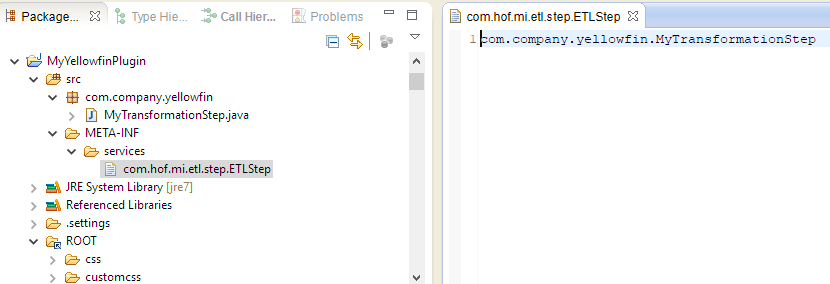
- Under the WEB-INF/src folder, create a new folder and call it META-INF. Create a new folder called services within this one.
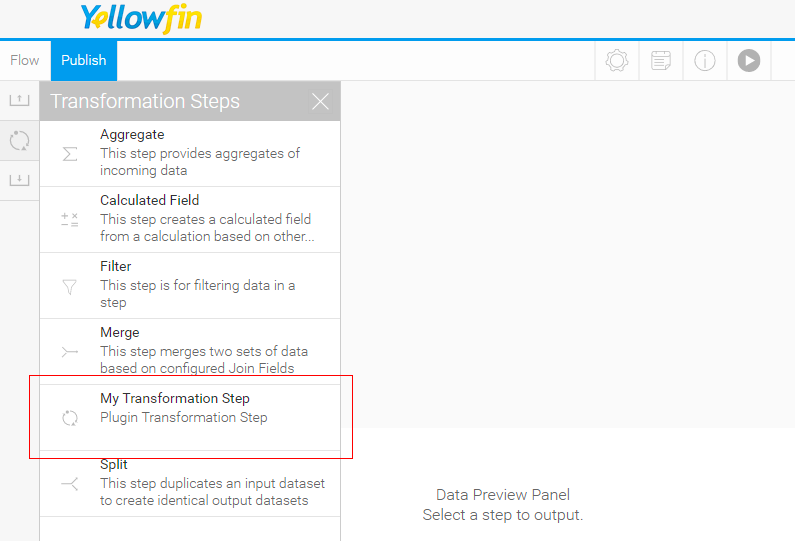
Create the following folder structure under src: META-INF/services. Depending on which plugin is being developed, create a file with the full fully qualified name of the plugin interface , in the services directory. See the table below for all available plugin options:
Yellowin Plugin
Interface
Description
Transformation Step com.hof.mi.etl.step.ETLStep A Step step which may be used in the Data Transformation module. Analytic Advanced Function com.hof.mi.interfaces.AnalyticalFunction Analytic Functions Advanced functions used in Reports. Data Type Converter com.hof.mi.interfaces.Converter Converts used Conversion of data types, done at the View Level and in the Data TransformationsTransformation module. Custom Formatter com.hof.mi.interfaces.CustomFormatter Formatting Custom formatting used in Reports. Data Profiler com.hof.mi.interfaces.DataSuggestionPlugin Profile data for a field and and . Contains functionality to determine whether the implemented suggestion is applicable.
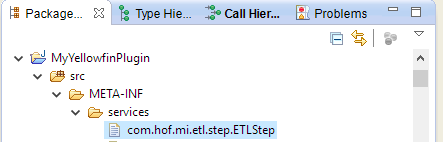
Icon Set com.hof.mi.interfaces.IconSet Defines an icon set for use with Report Alerts. Third-Party Connector com.hof.mi.thirdparty.interfaces.AbstractDataSource Connectors to create connections to an external API data sources. Canvas Widget com.hof.mi.widgetcanvas.interfaces.CanvasObjectTemplate Custom Widgets for widgets used in canvases in the Dashboard, Storyboard and Report OutputDesign modules. Source Platform com.hof.sources.SourcePlatform Define Source Types source types, such as JDBC, JNDI, OLAP etc. - For exampleinstance, if creating a Data Transformation Step, name the your file 'com.hof.mi.etl.step.ETLStep' if creating a Transformation Step.
- For exampleinstance, if creating a Data Transformation Step, name the your file 'com.hof.mi.etl.step.ETLStep' if creating a Transformation Step.
- Create the plugin class by implementing one of the interfaces given above. The fully qualified classname should be added to the services file corresponding to the interface.
So if the plugin being developed is a , for our Data Transformation Step example, add its fully qualfied class name qualified classname to META-INF/services/com.hof.etl.step.ETLStep
If necessary, another transformation step may be added .
You can add further transformation steps below this line, if required.
...
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Configure Tomcat
The next step is to set up your Tomcat configuration.
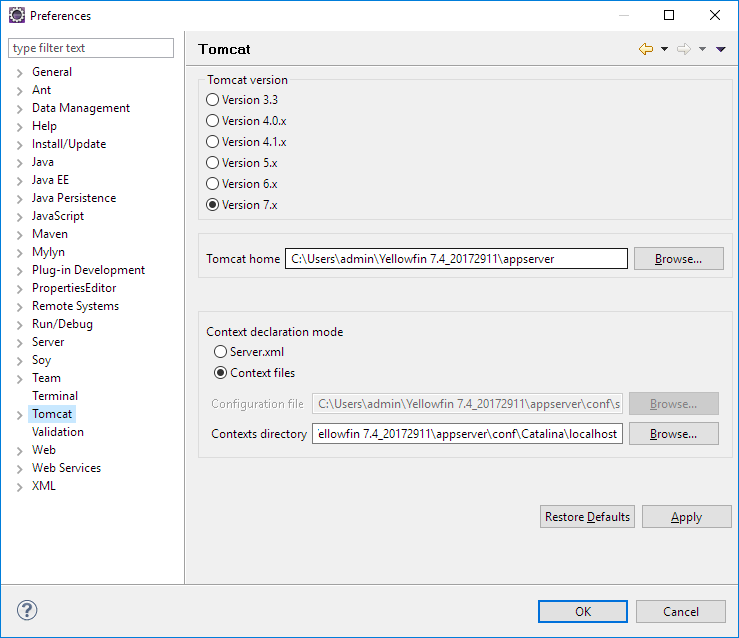
- Select Window Select Window > Preferences and go to the section for Tomcat.
- Set Tomcat Homehome to <Yellowfin Install directory>/appserver and appserver and Contexts directory to <Yellowfin Install directory>/appserver/conf/Catalina/localhost.
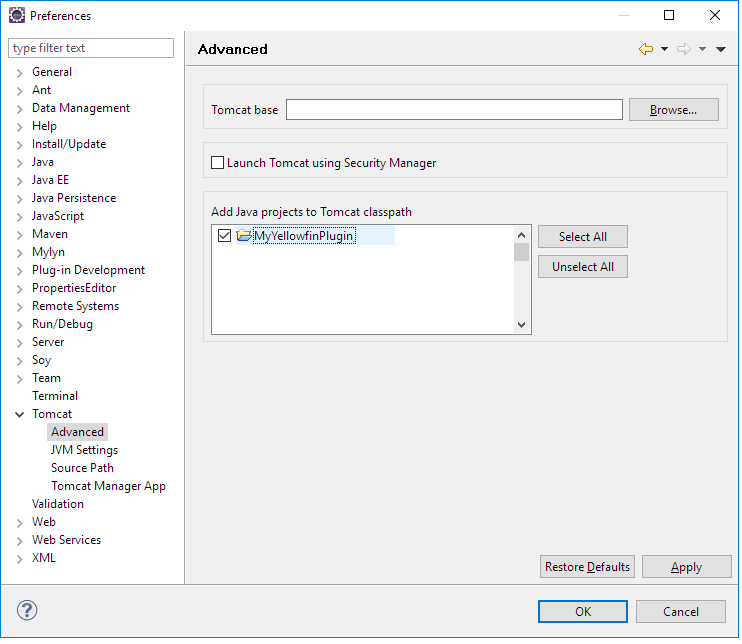
- Expand the Tomcat section in the left-side menu and click on Advanced. Add the plugin project to Tomcat's classpath.
- Adjust JVM Settings, if necessary . You (through the JVM Settings option on the left side). Tip: You could use this to increase the memory available for Tomcat.
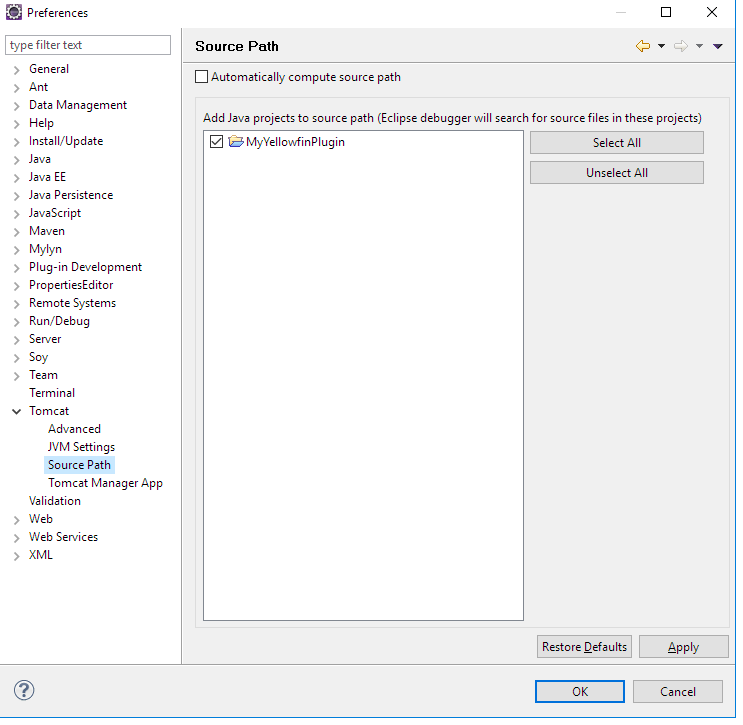
- Select Source Path and (in the left side menu) and add the plugin project.
- Click OK to save.
- Start up tomcat Tomcat from eclipse Eclipse using the buttons in the toolbar.
- The plugin will be now be available in Yellowfin.
| Tip |
|---|
Changes to code get reflected instantly, except when:
In these cases, Tomcat must be restarted to apply changes. |
...
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Packaging the Plugin
Once you've created your plugin, you will need to package it will all of its dependencies. The file extension extension should be in a specific file format that is supported in Yellowfin.
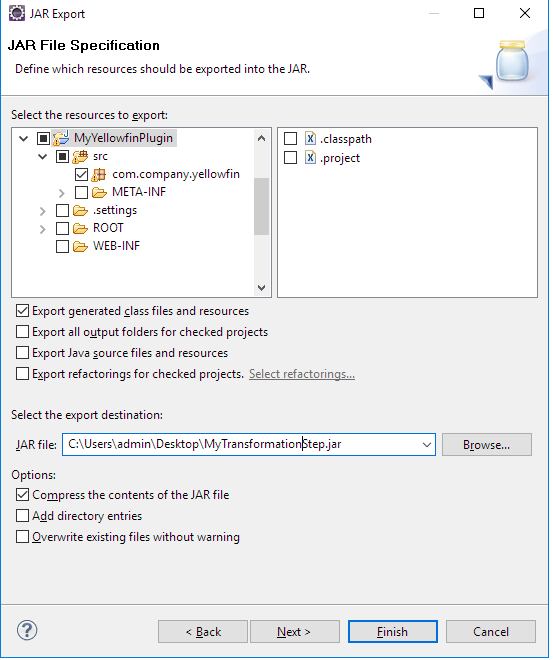
- Right-click on the project and select Export > JAR file.
- Select only the package(s) to be exported and nothing else.
- If the project has dependent JARs, put all of them and the Plugin JAR into one directory, zip into one archive, and give it the extension "yfp".
...
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
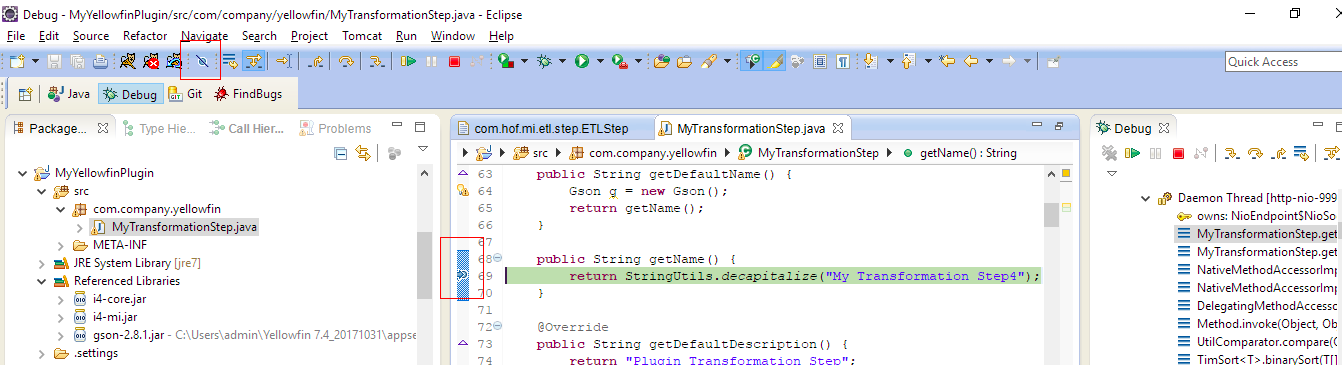
Debugging
Debugging is easy as the Eclipse Tomcat plugin starts Tomcat in the debug mode. Simply add breakpoints in code and ensure they are active.