Page History
...
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Docker architecture - typical Docker swarm cluster
The following diagram shows a typical Yellowfin cluster running in a Docker Swarm environment, which typically has the most components of our Docker deployment examples. Note that we’ve used Traefik in our architecture to route requests to the Yellowfin containers, but any container-aware proxy that makes use of sticky sessions could be used in its place.
...
- Docker Master Node
- Docker Swarm Worker Node(s): Yellowfin containers sit within the worker node or nodes of a Docker Swarm environment.
- The Yellowfin component: Yellowfin containers that make up the Yellowfin cluster have been deployed over multiple Docker worker/slave nodes in a Docker Swarm cluster. Unlike Traefik, there is no restriction to which nodes the Yellowfin containers can be deployed to. Depending on the Yellowfin deployment type that was chosen, the Docker environment will have one or more Yellowfin instances running, with those instances connecting to either the same database (for a clustered Yellowfin deployment) or different database (discrete instance deployment). In this diagram, they connect to the same database.
- DBMS: For performance reasons, we currently recommend not running the repository database in a Docker container for production workloads. Instead, we recommend a dedicated database server; for example, for AWS, an EC2 instance or using AWS RDS.
- Traefik: Traefik is a container-aware reverse proxy that runs on the manager node(s) in a Docker Swarm environment — due to it needing access to the Docker Swarm API — and handles the load balancing and sticky sessions for the Yellowfin containers. If you don’t wish to use Traefik (for example, you already use Nginx), you can use your own preferred load-balancing tool, provided it supports sticky sessions. We go into more detail about Traefik and Docker swarm later on.
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
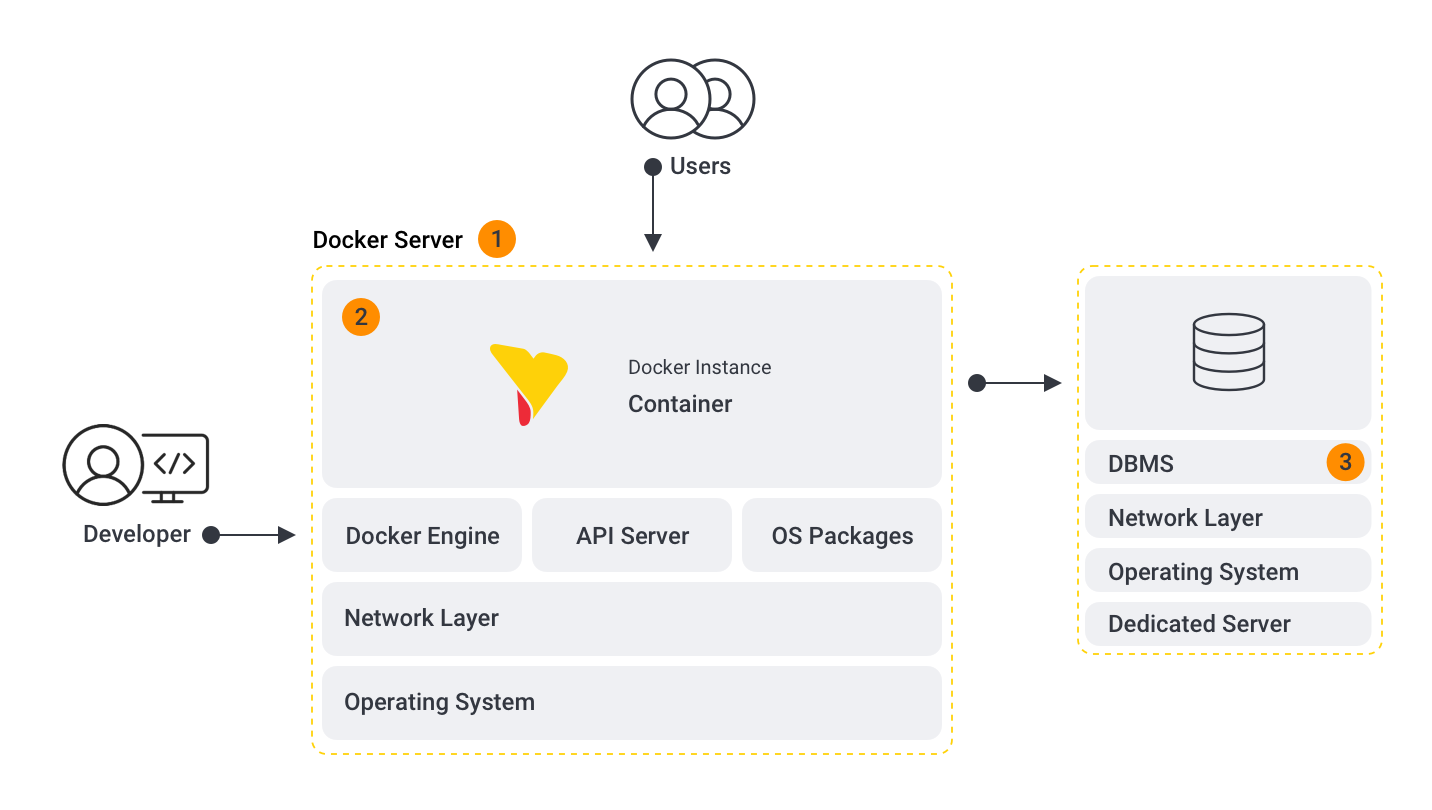
Docker architecture - typical single server instance
The following diagram shows a typical single Yellowfin instance running on a Docker server.
For single-instance deployments of Yellowfin on Docker Swarm, Traefik is an optional component, as with only one Yellowfin instance running, a reverse proxy is not required.
For single-instance deployments of Yellowfin on a Docker Server, Traefik can be deployed to route requests to the Yellowfin container (although we have not provided an example of it). See Traefik’s documentation on how to achieve this.
Breaking down the above diagram:
- Docker Server
- The Yellowfin component: a Yellowfin instance has been deployed in a container. The instance is connected to a separate database.
- DBMS: For performance reasons, we currently recommend not running the repository database in a Docker container for production workloads. Instead, we recommend a dedicated database server; for example, for AWS, an EC2 instance or using AWS RDS.
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Other scenarios
For multiple discrete Yellowfin instances on Docker Swarm, deploying Traefik is optional. If it is deployed in this situation, it can route requests to the discrete Yellowfin deployments, instead of exposing ports on the Docker Swarm cluster that route directly to the Yellowfin instances. For a single Docker server, the above architecture is similar, just that the Docker master and worker/slave nodes are one server. When running in this environment, whilst we have not provided an example of it, Traefik can be deployed to route requests to Yellowfin containers. See Traefik’s documentation on how to achieve this.
For a clustered Yellowfin deployment on a single Docker server, if the Docker environment can have an external load balancer that supports sticky sessions provisioned, then that can take the place of Traefik in this diagram.
If you’re using the Yellowfin All-In-One image, it does not require the external Yellowfin repository database, as the image comes embedded with its own.
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Preparing for deployment
Before deploying Yellowfin on Docker, make sure you’ve chosen which type of deployment suits your requirements. Choose from:
...
- a running Docker server with Docker Compose installed, or a Docker Swarm cluster; and,
- an understanding of Application Server Security.
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Section navigation
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Current topic - Install in a ContainerThe page is part of the Install in a Container topic contains the following pages, split by Docker and Kubernetes:
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Styleclass | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||